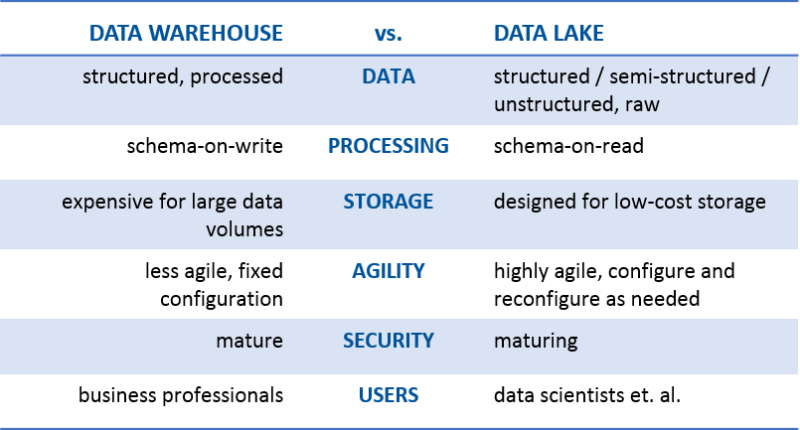
Data warehouse is the basis of Business Intelligence (BI). It not only provides the data storage of your production data but also provides the basis of the business intelligence you need. Almost all of the books today have very elaborated and detailed steps to develop a data warehouse. However, none of them is able to address the steps in a single page. Here, based on my experience in data warehouse and BI, I summarize these steps in a page. These steps give you a clear road map and a very easy plan to follow to develop your data warehouse.
Step 1. De-Normalization. Extract an area of your production data into a “staging” table containing all data you need for future reporting and analytics. This step includes the standard ETL (extraction, transformation, and loading) process.
Step 2. Normalization. Normalize the staging table into “dimension” and “fact” tables. The data in the staging table can be disposed after this step. The resulting “dimension” and “fact” tables would form the basis of the “star” schema in your data warehouse. These data would support your basic reporting and analytics.
Step 3. Aggregation. Aggregate the fact tables into advanced fact tables with statistics and summarized data for advanced reporting and analytics. The data in the basic fact table can then be purged, if they are older than a year.
Read more at One-Page Data Warehouse Development Steps
What do you think about this topic? Share your opinions below and subscribe us to get updates in your inbox.





















![The Impact of Big Data and Analytics on Manufacturing [ Infographic ]](http://supplychaininstitute.com/wp_sci/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/376431254_80_80.jpg)